This post was updated to reflect current trends and information.
Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) ACI eManifest
Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) requires all cargo transporters (Highway Carrier, Air Carrier, Marine Carrier, Rail Carrier, Freight Forwarder, Warehouse Operator, and Account Security Holder) to send electronically and in advance commercial information about their shipments in what is called Custom Manifest or Canadian Advance Commercial Information (ACI) eManifest. This measure is necessary to improve the security of international trade and to optimize commercial cross-border processes.
There are two possibilities to transmit electronically pre-arrival information to Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA). Companies may choose between:
Differences between CBSA Electronic Data Interchange and eManifest Portal
EDI and eManifest Portal have different terminologies, data requirements, and business rules. The differences are mainly because EDI and the eManifest Portal are based on two different technologies and interfaces.
EDI refers to the exchange of information, thus, companies using EDI can get statuses and receive notifications, while eManifest Portal refers to the submission of information only, and refers to Statuses.
Canada Border Services Agency CBSA EDI exchange
Similar to the US Customs and Border Protection (CBP) the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) is committed to both the ANSI X12 and UN/EDIFACT Electronic Data Interchange standards.
Communication Methods for Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) to CBSA
There are three options to transmit electronic commerce information to CBSA:
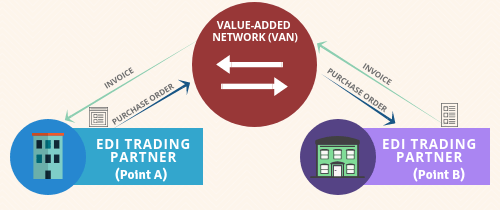
Value Added Network, or Direct Connect (DC) to the CBSA
Some VANs have an interconnect with the CBSA to allow EDI exchange with the trading partners and shipping companies; However, Direct Connect (DC) is an alternative that provides a special direct connection to CBSA. All new connections require an initial investment of $ 25,000 ($ 5,000) for customization.
Customs Internet Gateway (CIG)
CBSA has developed a Customs Internet Gateway (CIG) for transmitting and receiving data over the Internet. Clients must acquire certain encryption and decryption software, as well as develop or acquire protocol software to connect to the CIG. Customers will need to transfer data from the Canadian office, as the certificate is assigned only to the device in Canada.
Third-Party EDI Service Provider
For those companies who are unable or unwilling to transfer data directly to CBSA, there are third-party service providers who are setup and to transmit and exchange data with CBSA in both directions. These organizations offer various EDI solutions, and usually, offer a wide range of EDI services.
Information of Freight/Cargo Manifest for CBSA
The various information must be shown on Freight/Cargo Manifest. (paper form A6A) for example for Marine Carrier:
- Records the registered name of the vessel
- Port where the report is made (presented) – Canadian port where the vessel arrived or departed
- Nationality of ship
- Name of Master – Self explanatory
- Port of loading/discharge
- Final Destination (if on-carriage)
- Date of sailing from the port of loading
- Shipper, Consignee information
- Number of the ocean bill of loading
- Marks and numbers on each package
- Number and type of packaging, product description
- Gross shipping weight of cargo in each category by unit measure.
- Freight details, charges, etc.
In addition, all carriers and freight forwarders must have a carrier code issued by CBSA.
What Kind of Customs Documents Companies May Exchange via EDI with CBSA?
Depending on your business type and needs, you can submit and request different EDI documents and receive all acknowledgment and reject messages from CBSA:
– Highway carrier – cargo and conveyance documents for highway shipments.
– Air carrier – cargo, conveyance, house bills, and conveyance arrival documents for all air shipments.
– Marine carrier – cargo, conveyance, house bills, bay plan, and conveyance arrival documents for all marine shipments.
– Rail carrier – cargo, conveyance, house bills, and conveyance arrival documents for all rail shipments
– Warehouse operator – can request ACI notices.
– Freight Forwarders – house bill and close notifications for all shipments, all modes of transport
– Account Security Holder – receive notifications based on advanced trading data for all shipments and all modes of transport.
Timeframes for Submitting Custom Manifest to the CBSA

Air carriers – 4 hours
Air carriers transporting cargo to Canada must transmit information on cargo to CBSA at least four hours before arriving in Canada. If the duration of the flight is less than four hours, at the time of departure.
Highway carriers – 1 hour
Highway carriers that ship goods to Canada must transfer information about goods electronically to CBSA prior to arrival. CBSA must receive and verify cargo and transport data at least one hour before the cargo arrives at the border.
Marine carriers – 24 to 96 hours
Depending on the type and origin of the goods marine carriers carrying goods to Canada must submit cargo and conveyance information to CBSA within the prescribed time frame before arrival or before loading.
Rail carriers – 2 hours
CBSA must receive electronically cargo and conveyance information from rail carriers, within a minimum of two-hours before the conveyance arrives at the border.
The Best EDI Service Provider to Exchange EDI
At EDI2XML, we know that our first task is to provide innovative and effective solutions to solve the most difficult EDI task when crossing the border and saving you time and improving efficiency.
Are you need to submit your eManifest to Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA)? We have the solution! Contact us to learn more about ACI eManifest.


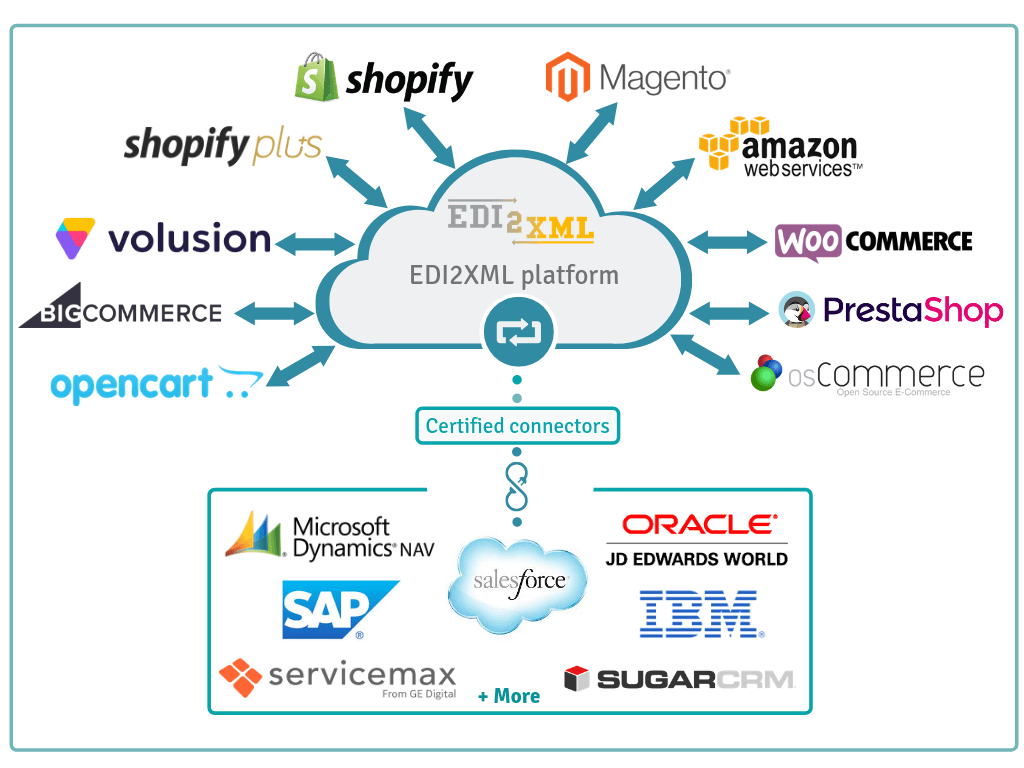
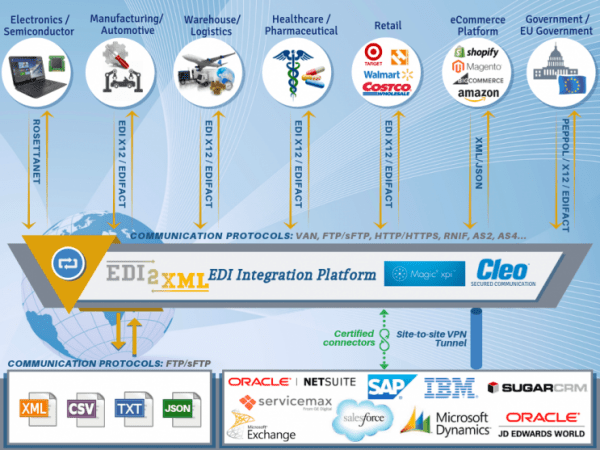



 Organizations of all types and sizes are able to utilize EDI. EDI communication is used in Government and various industries such as banking, healthcare, retail, automotive and others. Any company that buys, sells goods or services can potentially use EDI.
Organizations of all types and sizes are able to utilize EDI. EDI communication is used in Government and various industries such as banking, healthcare, retail, automotive and others. Any company that buys, sells goods or services can potentially use EDI.
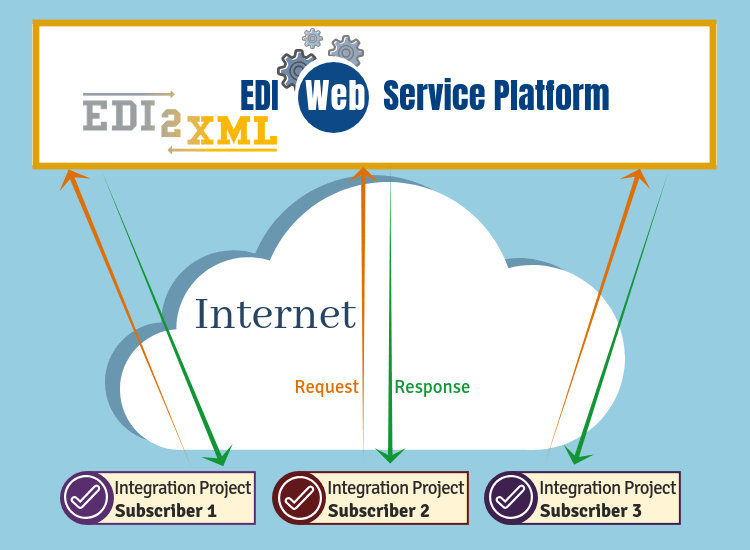
 Using SaaS EDI model customers do not pay for ownership of the software, but for renting it (i.e. using it through a mobile application or Web interface). The main advantage of the SaaS model for the company is the absence of costs associated with the installation, update, and maintenance of the equipment and software that is being used by the company.
Using SaaS EDI model customers do not pay for ownership of the software, but for renting it (i.e. using it through a mobile application or Web interface). The main advantage of the SaaS model for the company is the absence of costs associated with the installation, update, and maintenance of the equipment and software that is being used by the company.

 For many years we have seen the growing interest of the market towards a model called Software as a Service (
For many years we have seen the growing interest of the market towards a model called Software as a Service (

