Manufacturing and EDI: Introduction
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is an essential part of the modern manufacturing business process. EDI can speed up production, reduce labor and storage costs, and improve all manufacturing business processes.
In this article, we will analyze how and why EDI is used in manufacturing companies and how to get started with electronic data interchange.
Electronic data interchange (EDI) is the process of exchanging documents (such as purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, etc.) electronically with a business partner.
Why Use EDI in the Manufacturing Industry?

Every day manufacturing companies in all sectors face many challenges. Managing the procurement of raw materials and components for production, maintaining stocks at an optimal level, accelerating the turnover of finished products, quickly receiving payments, all these and many other challenges are being faced daily at most manufacturing enterprises.
That is why automation through the use of EDI helps to successfully manage many processes in production.
Manufacturing B2B Communication
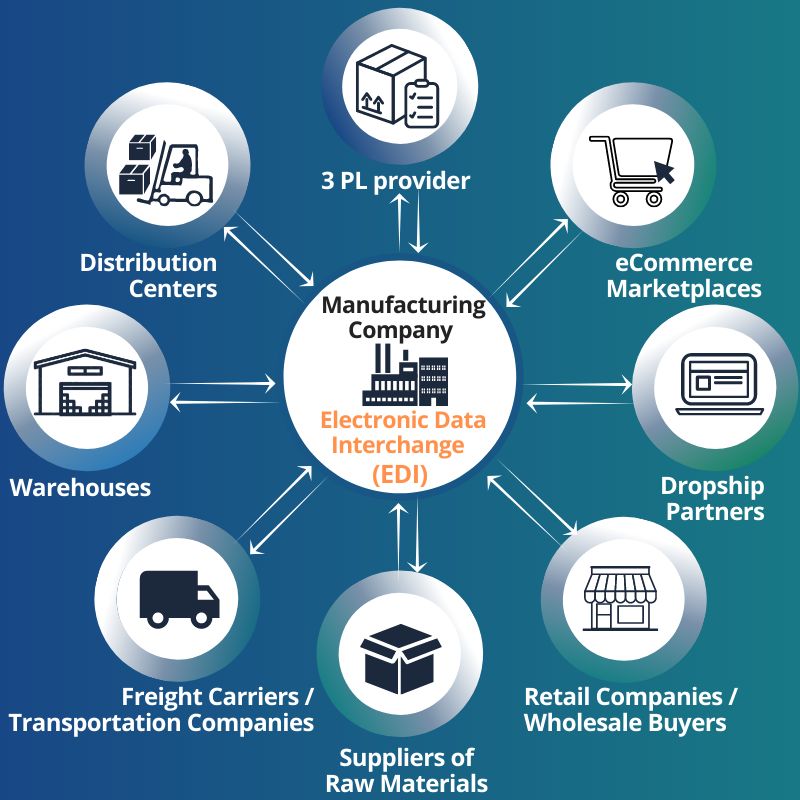
One of the particularities of a manufacturing company is that it can act both as a buyer when buying raw materials, components, and consumables, and as a seller when selling finished products.
A manufacturing company can have different EDI partners; it can exchange EDI documents with the following business partners:
- supplier of raw materials and component parts;
- wholesale buyer;
- distribution centers;
- retail companies;
- eCommerce marketplaces;
- dropship partners;
- warehouses / public warehouse;
- third-party logistics service providers (3 PL providers);
- freight carriers, transportation companies, and many others.
Manufacturing EDI Transactions
A manufacturing company may need to exchange bi-directional EDI transactions with different business partners. The type and number of EDI documents vary according to the business processes within the manufacturing company.
Below is a list of EDI documents for manufacturing; Some of them are used only for manufacturing enterprises, while others are being widely used in any business.
- EDI 196 – Contractor Cost Data Reporting
- EDI 830 – Planning Schedule / Material Release
- EDI 832 – Price/Sales Catalog
- EDI 844 – Product Transfer Account Adjustment
- EDI 846 – Inventory Inquiry/Advice
- EDI 849 Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment
- EDI 850 – Purchase Order
- EDI 852 – Product Activity Data
- EDI 855 – Purchase Order Acknowledgment
- EDI 856 – Advance Shipment Notice
- EDI 860 – Purchase Order Change
- EDI 861 – Receiving Advice/Acceptance Certificate
- EDI 862 – Shipping Schedule
- EDI 866 – Production Sequence
- EDI 867 – Product Transfer and Resale Report
- EDI 869 – Order Status Inquiry
- EDI 870 – Order Status Report
- EDI 894 – Delivery/Return Base Record
- EDI 895 – Delivery/Return Acknowledgment or Adjustment
- EDI 940 – Warehouse Shipping Schedule
- EDI 943 – Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice
- EDI 944 – Warehouse Receipt Advice
- EDI 945 – Warehouse Ship Advice
- EDI 997 – Functional Acknowledgment
As stated above, you will probably only need to integrate some of the EDI documents I listed above to automate your business processes and establish an electronic document exchange with your trading partner.
6 Essential EDI Documents for Manufacturing
What are the most common EDI documents used in manufacturing? As mentioned above, different manufacturing companies may use various sets of EDI transactions based on their own business processes and manufacturing characteristics. However, there are some basic EDI transactions that most manufacturing companies use.
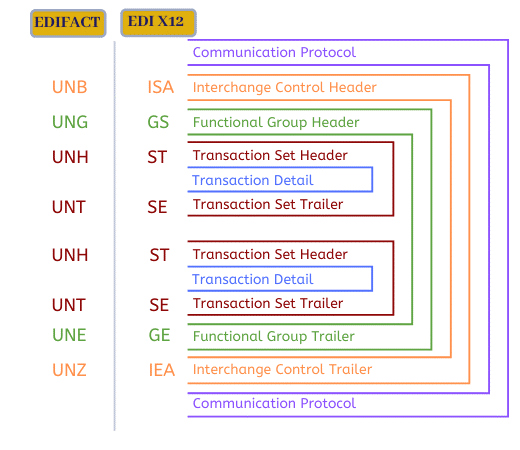
Below you will find the 6 EDI transactions used in manufacturing in the ANSI X12 standard (which is widely used in North America), and their equivalent in the EDIFACT standard for Europe.
1. EDI X12 830 – Planning Schedule with Release /EDIFACT (SLSFCT) – Sales forecast message
EDI 830 / EDIFACT( SLSFCT) transmits forecast data related to products, such as location, period, product identification, price, quantity, market sector information, etc.
This enables the recipient to process the data automatically and utilize it for production, planning, marketing, analytics, etc…
2. EDI X12 850 – Purchase Order / EDIFACT (ORDERS) Purchase Order Message
EDI 850 / EDIFACT (ORDERS) is the most commonly used EDI document, not just in the manufacturing industry, but across all industries since it is used when ordering goods. In the case of manufacturing companies, EDI 850 can be used either as an incoming or outgoing EDI document.
– Incoming EDI 850 is sent from the buyer to the manufacturing company when ordering finished products.
– Outgoing EDI 850 is sent by the manufacturing company to its supplier of raw materials or components.
The purchase order contains all the information about the ordering product such as item description, price, and quantities, payment terms, shipping details, requested delivery date, etc.
3. EDI X12 855 – Purchase Order Acknowledgement / EDIFACT (ORDRSP) Purchase Order Response)
EDI 855/ EDIFACT (ORDRSP) is an EDI transaction set that sellers send to a buyer as a response to a purchase Order X12 850/ EDIFACT (ORDERS), to confirm or reject the delivery of products.
PO Acknowledgement (855) is based on EDI 850 and contains similar information about the products, buyer, and seller information, order confirmation number.
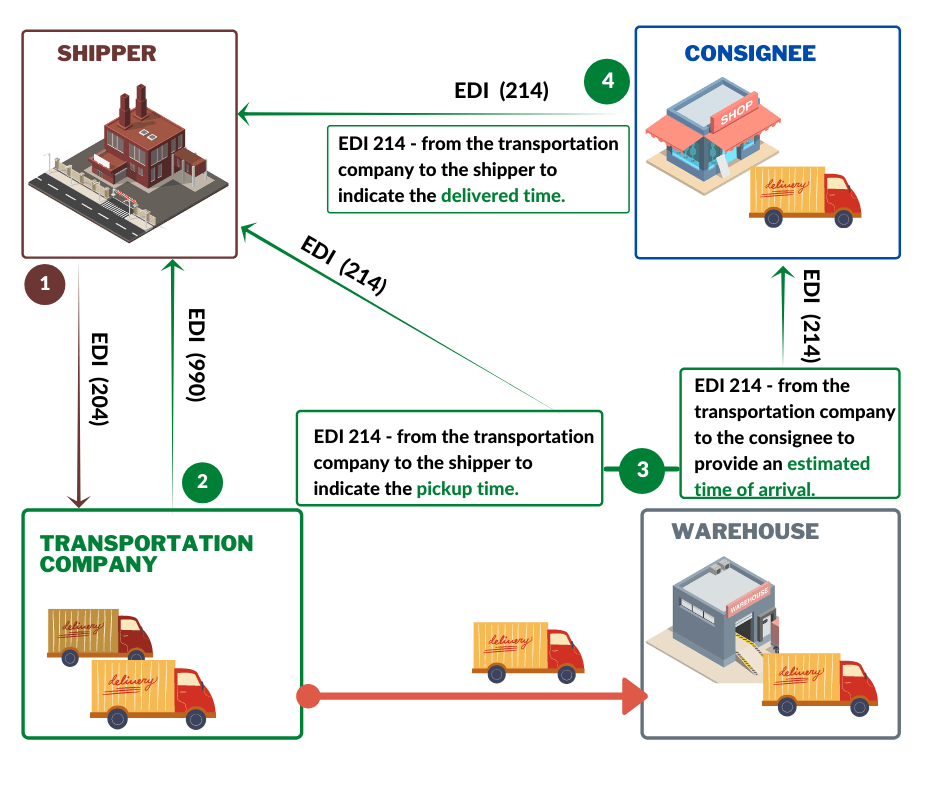
4. EDI X12 856 – Advance Shipment Notice (ASN) / EDIFACT DESADV Despatch advice message
EDI 856 message should be sent immediately after the shipment leaves the supplier’s premises.
The ASN 856 includes information about the contents of the delivery, the order, the packaging method, and the product description.
EDI 856 simplifies and speeds up the process of receiving goods, providing details about cargo, transferring information about shipments, and tracking the delivery.
5. EDI X12 810 – Invoice / EDIFACT (INVOIC) – Invoice
EDI 810 / EDIFACT (INVOIC) sent by the seller to the buyer to receive payment for goods provided.
In the case of a manufacturing company, EDI 810 can be used as an outgoing document from the manufacturing company to the buyer of the finished product, or as an incoming document from the raw material supplier to the manufacturing company.
6. EDI X12 EDI 846 – Inventory Inquiry/Advice / EDIFACT INVRPT – Inventory Inquiry/Advice
EDI 846 is sent by a manufacturer to inform its business partners (dealers, distributors, retailers, etc.) of current and future stock levels.
EDI 846 transmits full information about the product such as item description, quantity available in stock, price, as well as quantity forecasted, quantity sold already.
EDI Integration with Manufacturing Software, ERP, or CRM
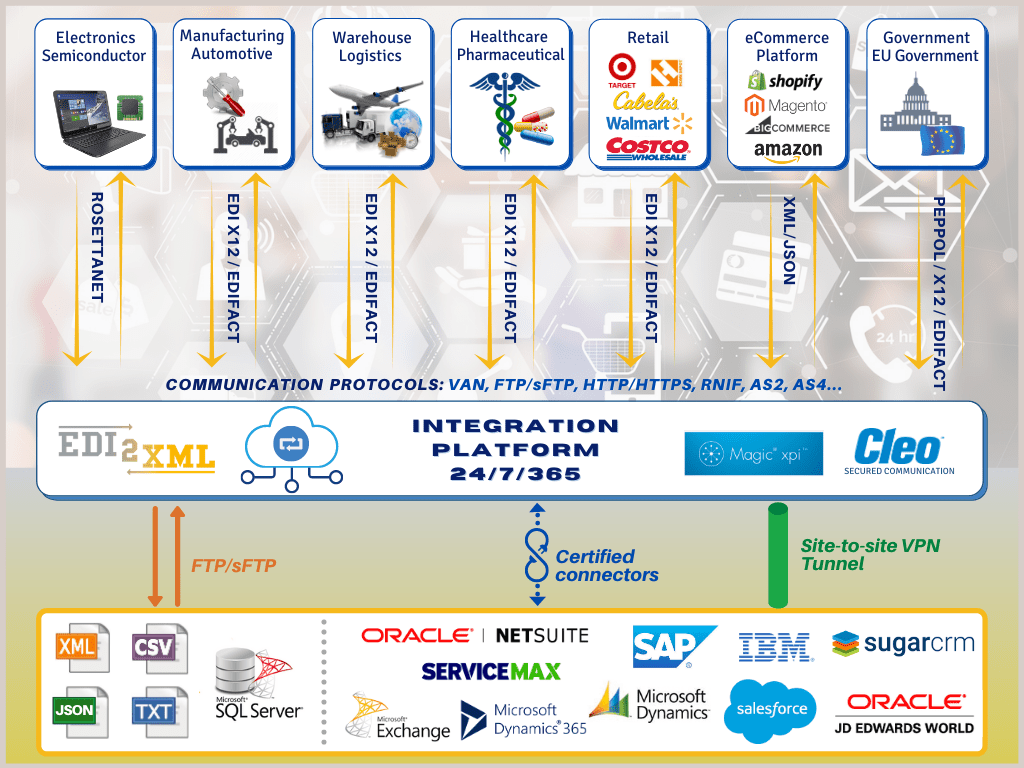
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is a powerful tool that can greatly streamline business processes, particularly when it comes to manufacturing. By integrating EDI with manufacturing software, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, manufacturers can improve efficiency and accuracy in areas such as order management, inventory control, and invoicing. EDI allows for the automated exchange of data between systems, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors. This integration can also help manufacturers better manage their supply chain, by providing real-time visibility into inventory levels and order status.
Get even more EDI benefits and improve your production efficiency by integrating EDI with your manufacturing software or your ERP, CRM, or accounting system. We can rapidly Integrate EDI with:
- Salesforce Cloud
- JD Edwards EnterpriseOne
- Oracle ERP Cloud
- SAP / SAP S4HANA
- Dynamics 365
- Oracle NetSuite
- DBA manufacturing software and many other
Overall, integrating EDI with manufacturing software, ERP, and CRM systems can help manufacturers improve productivity, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
We can connect EDI to any of your business systems in the cloud, on-premises, or in hybrid deployments using a no-code, low-maintenance approach that allows the manufacturing company to maximize the ROI from EDI.
Manufacturing Document Processing Automation with EDI Service Provider

An EDI integration and service provider, such as EDI2XML, can take over the entire task of exchanging EDI documents with your business partners.
EDI2XML can take care of all the EDI integration steps: from planning the EDI project to designing the file format that the customer requests (XML, TXT, CSV), to connectivity and full-cycle testing with the trading partner.
With our cloud-based fully managed EDI service we receive EDI files on behalf of our customers from its trading partners, convert incoming documents to the necessary format (XML, CSV, TXT, JSON, etc.) then push converted files directly to the business system of our customer.
Benefits of using EDI in Manufacturing
EDI has numerous business benefits for manufacturing companies, which includes:
– Accuracy. Reduce human interaction and errors associated with manual data entry. Thus, by automating the exchange of EDI documents, you can eliminate manual data entry and significantly reduce costs.
– Back-office productivity. Eliminating the need to store and manage physical documentation, and reducing transaction times.
– Production productivity. Through the use of EDI, manufacturing companies are achieving significant reductions in response/cycle times.
– Improve supply chain. EDI helps streamline processes throughout the supply chain and improve all operational processes in manufacturing.
– Improving business relationships with your retailers, wholesalers, and customers.
EDI integration helps to significantly improve logistics and production processes: from the purchase of raw materials to sales support and financing.
USEFUL: With our cloud-based Fully Managed EDI Service, we guarantee cost-effective initial and ongoing EDI service costs. Request our Fully Managed EDI Service Pricing Plans here
EDI Integration for Manufacturing with Any Trading Partner
As an EDI service provider with over 20 years of experience, we help our clients exchange EDI documents with their trading partners in the most efficient and cost-effective way. We can set up the exchange of EDI documents with any company, anywhere in the world, and no matter what industry it operates in.
Contact us for your first free consultation with one of our EDI integration experts.