Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has revolutionized the way businesses exchange information and collaborate with their business partners. EDI 404 (X12) – Rail Carrier Shipment Information is a transaction set that enables rail carriers to exchange shipment information with their trading partners.
In this article, we will explore EDI X12 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information in detail, including its purpose, format, segments, and benefits.
What is an EDI X12 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information?
The Rail Carrier Shipment Information EDI 404 is an electronic document or transaction set that allows rail carriers and their trading partners to exchange shipment information. This transaction set is part of the Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) X12 standard.
EDI 404 is a transaction set that is specifically designed for rail transportation companies. It is not used in other modes of transportation, such as trucking or air transportation.
Purpose of EDI 404 (X12) Rail Carrier Shipment Information
The primary purpose of EDI 404 is to facilitate the exchange of rail carrier shipment information between trading partners. EDI 404 provides detailed information about a shipment that is being transported by rail, including its origin, destination, routing, and other related details.
According to X12, chartered by the American National Standards Institute the EDI 404 transaction set can be used to transmit rail carrier bill of lading information to the railroad.
This is the initial shipment order between the shipper and the rail carrier and can be used as an equipment release notice and/or legal bill of lading.
The EDI 404 document is particularly useful for companies that need to track and manage their shipments efficiently.
By receiving shipment information electronically in a standardized format, companies can automate many of their business processes and reduce manual data entry errors. This can help to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and increase overall productivity.
EDI 404 (X12) Segments and Data Elements
The EDI X12 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information transaction set transmits various data elements related to a rail shipment. The transaction set follows a standard format that includes segments, data elements, and composite data structures. The segments are the building blocks of the transaction set and contain specific information about the shipment.
The data elements provide additional details within each segment, while the composite data structures combine multiple data elements into a single data element for easier processing.
Here are some examples of the data that can be transmitted through the EDI X12 404 transaction set according to BNSF 404 Implementation Guideline.
Segments and Data Elements:
- ISA Interchange Control Header
- GS Beginning Segment.
- ST Transaction Set Header
- ZC1 Beginning Segment for Data Correction or Change
- BX General Shipment Information
- BNX Rail Shipment Information
- M3 Release Information
- N9 Reference Number
- CM Cargo Manifest.
- M1 Insurance Details.
- DTM Date/Time Reference
- N7 Equipment Details (N7 Loop)
- EM Equipment Characteristics
- VC Motor Vehicle Control (N7/VC Loop)
- N1 Name (N7/VC/N1 Loop)
- N3 Address Information.
- N4 Geographic Information.
- H3 Special Handling Instructions
- M7 Seal Numbers
- N5 Car Ordered
- IC Intermodal Chassis Equipment
- IM Intermodal Information
- M12 In-Bond Identifying Information
- EI Empty Car Disposition – Pended Destination Consignee (E1 Loop)
- E4 Empty Car Disposition – Pended Destination City
- E5 Empty Car Disposition – Pending Destination Route
- PI Price Authority Identification
- GA Canadian Grain Information
- REF Reference Identification (REF Loop)
- N10 Quantity and Description
- N1 Name
- N3 Address Information
- N4 Geographical Information
- NA Cross Reference Equipment
- F9 Origin Station
- D9 Destination Station
- N1 Name (N1 Loop)
- N2 Additional Name Information.
- N3 Address Information
- N4 Geographic Information
- REF Reference Identification
- PER Administrative Communications Contact
- BL Billing Information
- S1 Stop Off Name (S1 Loop)
- S2 Stop Off Address
- S9 Stop Off Station
- N1 Name (S1/N1 Loop)
- N2 Additional Name Information
- N3 Address Information
- N4 Geographic Location
- PER Administrative Communications Contact
- R2 Route Information
- R9 Route Code
- E1 Empty Car Disposition Pended Destination Consignee (E1 Loop)
- E4 Empty Pended Destination Pended Destination City
- E5 Empty Car Disposition Pended Destination Route
- PI Price Authority Information
- H3 Special Handling Instructions
- PS Protective Service Instructions
- LX Assigned Number (LX Loop)
- L5 Descriptions, Marks,and Numbers
- L0 Line Item, Quantity, and Weight (L0 Loop)
- MEA Measurements
- L1 Rate and Charges
- PI Price Authority Information
- X1 Export License
- T1 Transit Inbound Origin (T1 Loop)
- T2 Transit Inbound Lading
- T3 Transit Inbound Route
- T6 Transit Inbound Rates
- T8 Free Form Transit Data
- L3 Total Weight and Charges
- LS Loop Header
- LH1 Hazardous ID Information (LH1 Loop)
- LH2 Hazardous Classification
- LH3 Proper Shipping Name
- LFH Free Form Haz Mat Information
- LEP EPA Required Data
- LH4 Canadian Hazardous Requirements
- LHT Transborder Hazardous Requirements
- LHR Haz Mat ID Reference Numbers
- PER Administrative Communications Contact
- LE Loop Trailer
- PER Admin. Communication Contact (Haz Mat Shipments Only)
- LH2 Hazardous Classification Information
- LHR Haz Mat ID Reference Numbers (Haz Mat Shipments Only)
- LH6 Hazardous Certification
- XH Pro Forma B13 Information
- X7 Customs Information
- SE Transaction Set Trailer
- GE Functional Group Trailer
- IEA Interchange Control Trailer
It’s important to note that each rail carrier may have slightly different requirements for their EDI 404 transaction set. Therefore, it’s essential to use the implementation guideline provided by the specific rail carrier that you are working with to ensure that your data is properly formatted and transmitted.
Implementation Guideline will provide you with the specific data elements, segments, and codes that rail carriers require for the EDI 404 transaction set.
It can also provide guidance on the technical aspects of transmitting the data, such as the file format, transmission protocols, and testing procedures.
EDI 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information Document Exchange Workflow
In order to use EDI X12 404, both the shipper and the carrier must have the necessary technology and systems in place to support the transaction set.
Here’s a possible workflow for the exchange of an EDI 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information Document:
EDI 404 Preparation
The shipper (sender) prepares the shipment and creates an EDI 404 document with the relevant information, such as the shipper and consignee names and addresses, the description of the goods, the weight and dimensions, the origin and destination locations, and the carrier information. The document is formatted according to the EDI X12 standard and the specific requirements of the carrier using sender’s internal system or a third-party EDI services.
EDI 404 Transmission
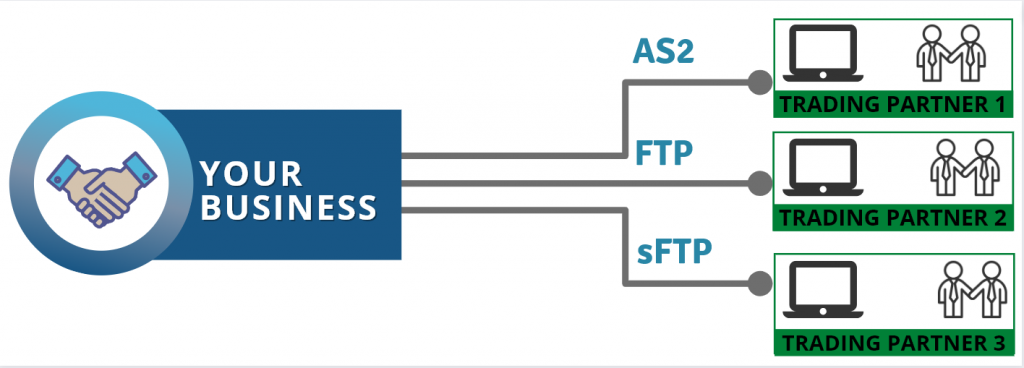
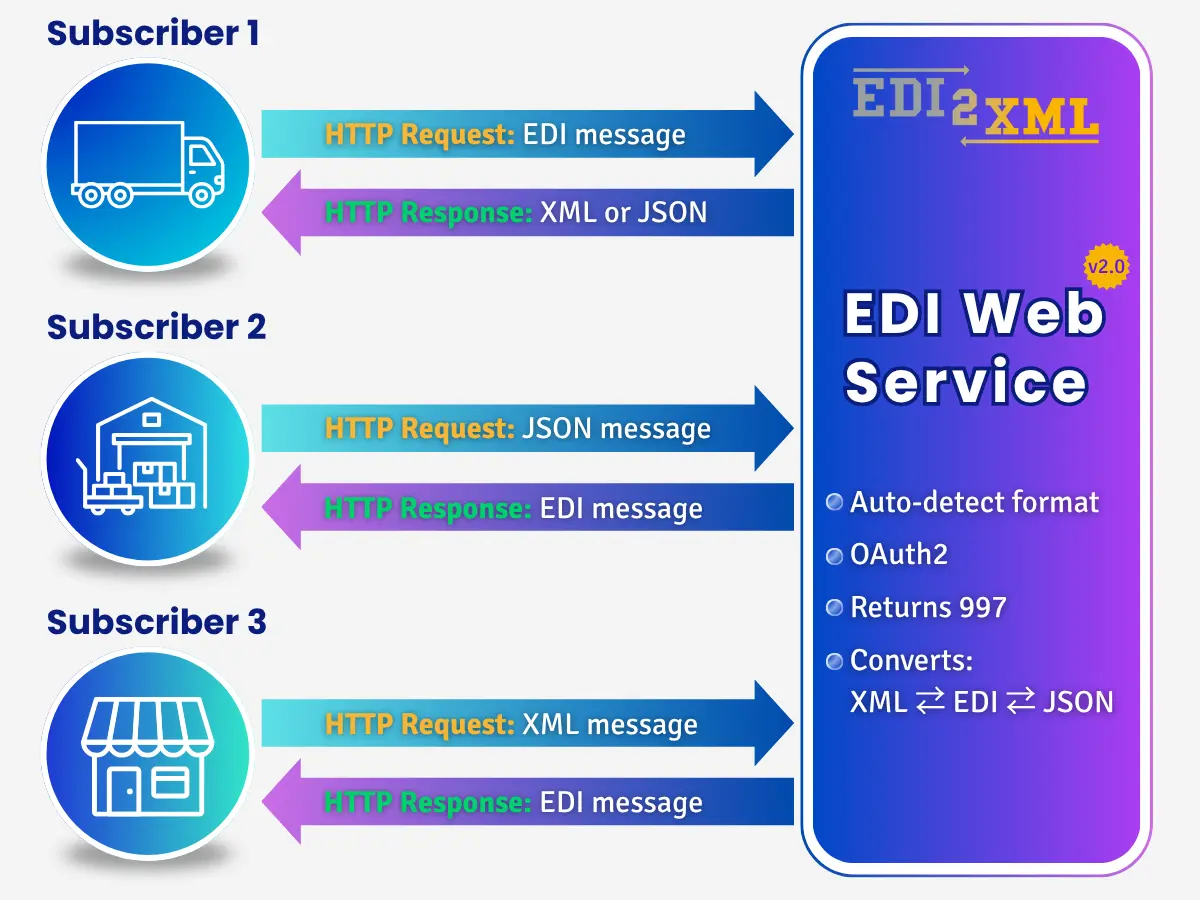
There are several methods to transfer an EDI document to a business partner. Here are some of the most common methods:
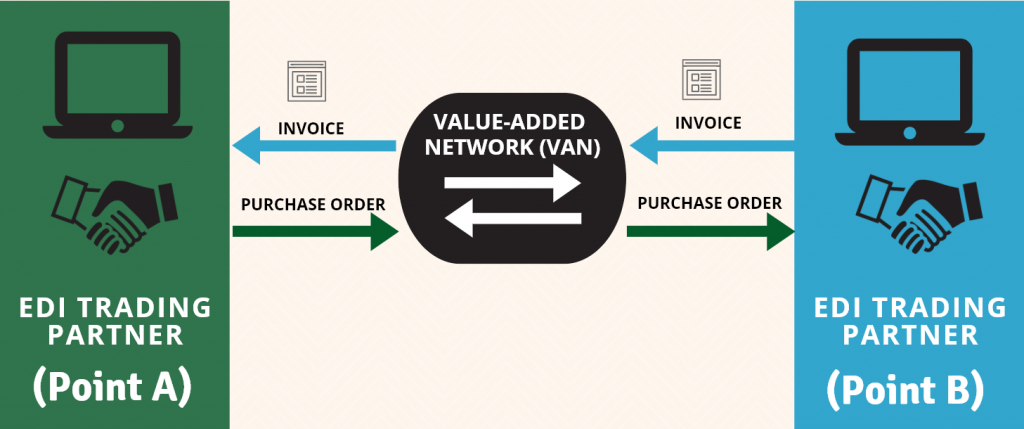
- Value-Added Network (VAN): This is a third-party network that acts as a middleman between trading partners to transmit EDI documents securely. The VAN providers charge a fee for their services.
- AS2 (Applicability Statement 2): This is a popular protocol for transmitting EDI documents over the internet using encryption and digital certificates. AS2 is a secure and reliable method for EDI document exchange.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): FTP is a standard protocol used to transfer files over the internet. EDI documents can be transmitted using FTP by configuring a server and client for file exchange.
- Web-based EDI: (REST API) Some EDI providers offer web-based solutions that allow companies to exchange EDI documents through a web interface. This method allows you to quickly start exchanging EDI documents with your business partners.
- Direct connection: EDI documents can be transmitted directly between two systems using a point-to-point connection. This method requires setting up a dedicated connection between the two systems.
EDI 404 Receive, Validation, and Acknowledgment
The carrier receives the EDI 404 document, validates its syntax and structure, and processes it through their EDI system.
Once the receiver has successfully received and validated the EDI 404 document, they should send back an acknowledgment message (EDI 997 document) to the sender to confirm the receipt and acceptance of the EDI 404 document.
The acknowledgment may include a unique transaction ID, the date and time of receipt, and any relevant status codes or error messages. The sender may use this information to track the progress of the shipment and to resolve any issues that may arise.
EDI 404 Processing
The carrier processes the shipment based on the information provided in the EDI 404 document, such as scheduling the pickup, assigning a rail car, routing the shipment, and generating the necessary documents and labels.
The carrier may also update its internal systems and communicate with other parties involved in the shipment, such as the consignee, the customs authorities, or other carriers in case of intermodal transportation.
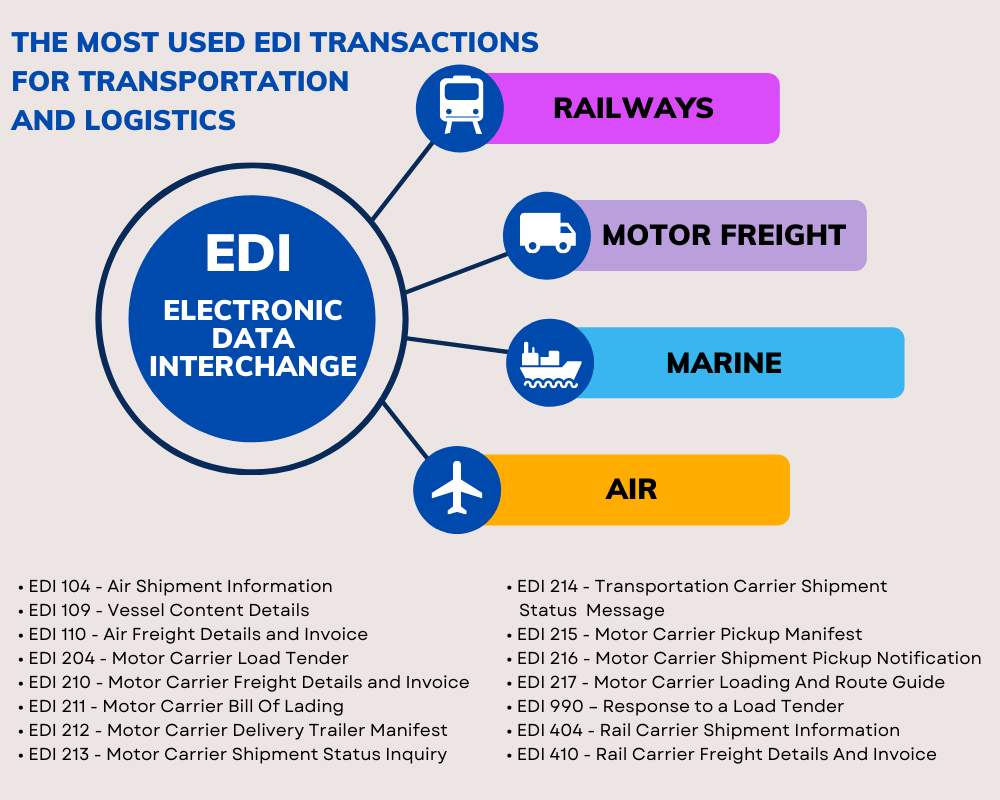
Specific EDI Documents for the Rail Industry
In addition to the EDI 404 discussed in this article, here are some of the most commonly used EDI X12 transaction sets in the railroad industry:
410 Rail Carrier Freight Details and Invoice: This transaction set is used to transmit billing and payment information related to rail transportation services.
417 Rail Carrier Waybill Interchange: This transaction set is used to exchange waybill information between rail carriers, including origin and destination locations, equipment requirements, and shipment details.
418 Rail Advance Interchange Consist: This transaction set is used to provide advance notice of railcar movements between rail carriers.
419 Advance Car Disposition: This transaction set is used to provide advance notice of railcar movements to car owners, lessees, or shippers.
422 Shipper’s Car Order: This transaction set is used by shippers to order railcars from the rail carrier.
423 Rail Industrial Switch List: This transaction set is used to provide information about railcar movements within an industrial facility.
424 Rail Carrier Services Settlement: This transaction set is used to provide settlement information for rail transportation services.
Note that this list is not exhaustive, and there may be other EDI X12 transaction sets used in the rail industry depending on the specific needs of the trading partners involved.
While the EDI transactions listed above are unique to rail transportation, there are other EDI transaction sets that are used in the transportation industry more broadly, such as EDI 204 (Motor Carrier Load Tender), EDI 210 (Motor Carrier Freight Details and Invoice), and EDI 214 (Transportation Carrier Shipment Status Message).
You can find out more information about EDI documents for transportation or other industries in the article EDI for Specific Industries.
Benefits of EDI/X12 404
EDI X12 404 offers several benefits to rail carriers and their trading partners. Some of the key benefits include:
- Improved Efficiency: By automating the exchange of shipment information, rail carriers can improve their operational efficiency and reduce errors and delays in the shipment process.
- Cost Savings: EDI X12 404 can help reduce costs associated with paper-based processes, such as printing, mailing, and storage.
- Enhanced Visibility: With EDI X12 404, rail carriers and their trading partners can gain real-time visibility into shipment status updates, equipment and routing details, and transportation charges.
- Faster Payments: EDI X12 404 can help accelerate the invoicing and payment process by providing accurate and timely information about transportation charges.
EDI X12 404 Sample File
This is an example of an EDI file from BNSF 404 Implementation Guideline “USING ASC X12 TRANSACTION SET 404 VERSION 004010 10/01/98”
Sample EDI/X12 404
Minimal data requirements for a carload bill of lading
- GS*SR*CUSTOMERX*BNSF*20230101*1520*2315*X*004010
- ST*404*4567
- BX*00*R*PP**BNSF*L*B*N
- BNX*A
- M3*B*20230101*1520*CT
- N9*RP*AWI233**20230101*1520*CT
- N9*BM*HGP2684**20230101*1520*CT
- N7*ATSF*111598*195320*N*******RR
- F9** CHICAGO *IL
- D9**BOSTON*MA
- N1*CN*CUSTOMER X
- N4*BOSTON*MA
- N1*SH*ABC CUSTOMER
- N4* BOSTON*MA
- PER*NT*JEAN DUPONT*TE*098-765-4321
- R2*BNSF*S****R
- LX*1
- L5*1* WALLBOARD *1301210*T
- L0*1*******1*CLD
- PI*CT*12345***BNSF*BNC
- SE*21*2315
- GE*1*2315
- GS*SR*CUSTOMERX*BNSF*20230101*1520*1315*X*004010 – This line contains the GS segment which is a functional group header. It identifies the sender (CUSTOMERX) and the receiver (BNSF), as well as the date and time (20230101 15:20) and the version of the EDI standard used (004010).
- ST*404*4567 – This line contains the ST segment which is a transaction set header. It identifies the type of document (404) and a unique control number (4567) assigned by the sender.
- BX*00*R*PP**BNSF*L*B*N -This line contains the BX segment which indicates the beginning of a transaction set. It specifies the version of the EDI standard used (00) and General Shipment Information, including the type of transaction (R for railroad) and the carrier (BNSF).
- BNX*A – This line contains the BNX segment which is used to identify and track the progress of the shipment.
- M3*B*20230101*1520*CT – This line contains the M3 segment which provides information about the shipment, including the date and time it was shipped (20230101 15:20) (CT for central time).
- N9*RP*AWI233**20230101*1520*CT – This line contains the N9 segment which identifies a reference number (AWI233) for the shipment and provides the date and time it was shipped (20230101 15:20)
- N9*BM*HGR2088**20230101*1520*CT – This line contains the N9 segment which identifies a reference number (HGR2088) BM – bill of lading number and provides the date and time it was shipped (20230101 15:20)
- N7*ATSF*111598*195320*N*******RR – This line contains the N7 segment which provides information about the equipment used to transport the shipment, including the the equipment number (111598), and the type of equipment (RR – for a railcar).
- F9**CHICAGO*IL – This line contains the F9 segment which provides information about the origin of the shipment, including the city and state (Chicago, Illinois)
- D9**BOSTON*MA – This line contains the D9 segment which provides information about the destination of the shipment, including the city and state (Boston, Massachusetts)
- N1*CN*CUSTOMER X– This line contains the N1 segment which identifies a party involved in the shipment (in this case, the consignee) and provides their name (CUSTOMER X).
- N4* BOSTON*MA – This line contains the N4 segment which provides information about the Geographic location of the consignee (in this case, Boston, Massachusetts).
- N1*SH*ABC CUSTOMER – This line contains the N1 segment which identifies a party involved in the shipment (in this case, the shipper – SH) and provides their name (ABC CUSTOMER).
- N4* BOSTON*MA – This line contains the N4 segment which provides information about the location of the shipper (in this case, Boston, Massachusetts).
- PER*NT*JEAN DUPONT*TE*098-765-4321– This line contains the PER segment which provides contact information for a person or department involved in the shipment. In this case, it is Jean Dupont, and its phone number (TE) is 098-765-4321.
- R2*BNSF*S****R – This line contains the R2 segment which provides Route Information and the equipment used to transport the shipment, including the carrier (BNSF) and the type of equipment (R for a railcar).
- LX*1 – This line contains the LX segment which identifies an Assigned Number.
- L5*1*WALLBOARD*1301210*T – This line contains the L5 segment which provides information about the product being shipped (descriptions, marks, and Numbers) in this case, WALLBOARD. T = Standard Transportation Commodity Code (STCC)
- L0*1*******1*CLD – This line contains the L0 segment which provides information about Line Item, Quantity and Weight. CLD – Car Load, Rail.
- PI*CT*12345***BNSF*BNC – Price Authority Information. CT – contract, BNSF – the carrier.
- SE*21*2315 – This line contains the SE segment which is a transaction set trailer. It specifies the number of segments in the transaction set (21) and a unique control number (2315) assigned by the sender.
- GE*1*2315 – This line contains the GE segment which is a functional group trailer. It specifies the number of transaction sets in the functional group (1) and a unique control number (2315) assigned by the sender.
EDI 404 Document for Rail Carrier Companies
Many companies in the transportation industry use EDI X12 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information to automate the exchange of shipment information with their trading partners. Here are a few examples of companies that use this transaction set:
- Union Pacific Railroad Union Pacific Railroad is one of the largest freight railroad networks in North America.
- Canadian National Railway Canadian National Railway is a transportation company that operates a comprehensive rail network in Canada and the United States.
- Norfolk Southern Corporation Norfolk Southern is a transportation company that operates a rail network in the eastern United States.
- BNSF Railway BNSF Railway is a freight transportation company that operates a rail network in North America.
- CSX Transportation CSX Transportation is a transportation company that operates a rail network in the eastern United States.
These are just a few examples of companies that use EDI X12 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information. Many other transportation companies also use this transaction set to automate the exchange of critical shipment data with their trading partners.
Conclusion: EDI X12 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information
In conclusion, understanding EDI X12 404 Rail Carrier Shipment Information is crucial for businesses operating in the logistics industry. As we have seen, it streamlines communication between rail carriers and shippers, making the transportation of goods more efficient and cost-effective.
At our company, we have many years of experience in EDI integration and can provide free EDI consultation to businesses looking to implement EDI X12 404 or any other EDI document. We understand the importance of staying up-to-date with industry developments and are committed to helping our clients achieve success in their logistics operations.
So if you’re looking to streamline your logistics processes and improve communication with your rail carriers, don’t hesitate to reach out to us for a consultation. We look forward to working with you and helping your business thrive in the ever-evolving world of logistics.