This post was updated to reflect current trends and information.
Why eCommerce Integration Matters for Growing Businesses
eCommerce platforms have been largely used by small and mid-sized enterprises, to sell their products and services to the booming consumer market (B2C) on the internet. Amazon and eBay for example, are among the most popular eCommerce platforms; for ease of operations and integration they offer different ways to exchange data between the trading partner and the platform. As an example, Amazon offers EDI integration capability, or Web service calls to exchange data or simple XML transactions. The most frequently asked question, by business owners, is: what is the best option to have a quick integration at a minimal cost with a maximum return on investment?
In this post I will explain the different integration mechanisms and share my opinion on how to decide which way to go. As a complementary article to this post, I invite you to read my previous post entitled Tips to Empower your eCommerce with great Supply Chain through EDI Integration to get more detailed advise about eCommerce and EDI integration to be able to build a strong SCM channel.
Let me start by quickly defining each of the above technical terms:
What is EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)
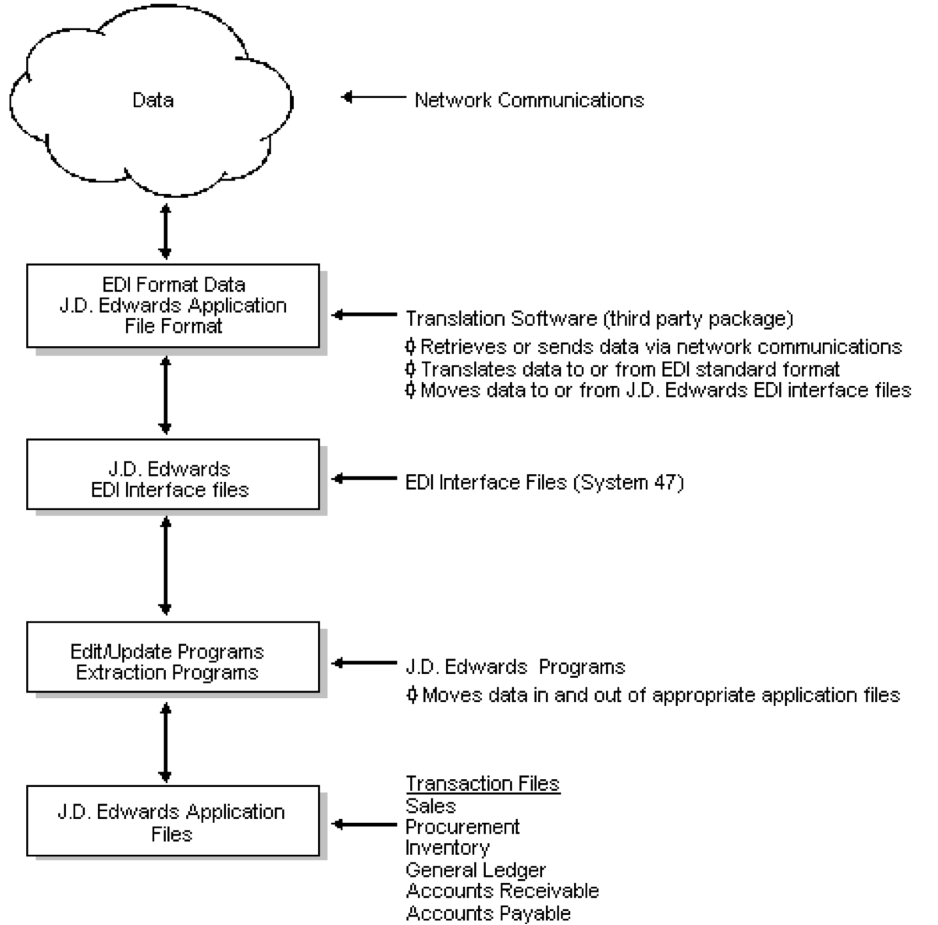
EDI is the oldest protocol used to exchange data between business partners. It has been standardized and heavily used for decades. It is very well ingrained in the manufacturing and retail verticals. Data in EDI format has a pre-defined format and structure. It is transmitted using different types of secured communication protocols (i.e. VAN, AS2, FTP, sFTP…).
Useful reading: What is EDI?
What is XML (Extensible Markup Language)
As defined by the W3Schools website , XML is a markup language much like HTML, meant to carry data, not to display data. It is designed to be self-descriptive, where users define their own XML tags to describe data. XML is a W3C recommendation. XML was created to structure, store, and transport information, in contrast to HTML that is meant only to display data in a web browser.
Since XML has been developed, it quickly became a popular means to transfer very well structured data between business partners. Thanks to its ease of use, and its descriptive aspect of the XML data format, it has been the preferred choice of many software vendors and applications used in integration projects.
Web services (SOAP and REST)
Wikipedia defines a Web service as “a method of communication between two electronic devices over a network. It is a software function provided at a network address over the web with the service always on as in the concept of utility computing”.
Web services are designed to support machine-to-machine interaction over a network, using different protocols, by sending and receiving “messages” using HTTP and XML in addition to other web-related standards.
Now for the technical use and interpretation of Web Services, it is simply triggering the execution of a program or function remotely, using the internet, and returning the result to the caller. In addition, Web services use XML in different formats to send structured data back and forth. The advantage of Web services is that it uses the internet as a communication and transport protocol, in addition to the XML structured language to format the data transmitted back and forth.
If you want to know more about different types of web services such as SOAP and REST and why EDI developers prefer use RESTful services, read our new article: Seamless EDI implementation through Web Services
Takeaways:
Web services enable real-time, machine-to-machine communication over the internet. They use HTTP and XML (or JSON in RESTful APIs) to exchange data between applications.
Modern platforms often rely on RESTful APIs for faster, lighter integration.
This method is ideal for businesses seeking flexibility and scalability across cloud-based systems.
Useful reading: What is EDI2XML web Service?
What Is eCommerce Integration?
eCommerce integration means the process of sending data from the eCommerce platform to an external system or platform, and receiving data into the eCommerce platform using an automated process. Integrating your ERP system or a company’s CRM system with the eCommerce platform enables the necessary data to be sent in both directions so that both systems can interact in a seamless way, without the need for human intervention. This will improve efficiency and enterprise capabilities to serve clients faster.
Useful reading: Tips to Empower your eCommerce with great Supply Chain through EDI Integration
How to Choose the Right Integration Method
In my opinion, there is no single rule when selecting an integration method. Any business owner, executive or integration consultant should ask the following technical questions before selecting a technology and protocol to integrate their eCommerce platform with their own system:
- What’s the expertise of my integration team?
- Are they familiar with EDI format and protocols as well as its business flow?
- Are they more familiar with XML and web services?
- What are the additional technical advantages that the enterprise would gain by selecting one versus the other?
- Are these advantages important issues for our business?
- What are the add-on costs for both options?
Basically, the decision comes down to evaluating the level of expertise of the integration team and their zone of technical comfort. From a technical perspective, there isn’t a perfect option. Of course, the business aspect of the decision is a major factor and sometimes, business reasons might outweigh technical reasons.
If you need more information or would like to discuss your eCommerce integration needs, I will be more than happy to provide a free 1-hour consultation.









 Salesforce is a cloud-based CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software system. It is very popular amongst enterprises of all sizes as it is best known for its openness for integration. Developers and integrators can read and write data using API and web services. Many companies use Salesforce as a unified tool for leads, campaigns, opportunities and customer tracking.
Salesforce is a cloud-based CRM (Customer Relationship Management) software system. It is very popular amongst enterprises of all sizes as it is best known for its openness for integration. Developers and integrators can read and write data using API and web services. Many companies use Salesforce as a unified tool for leads, campaigns, opportunities and customer tracking.


