This article will cover one of the critical EDI documents in Supply Chain Management, the EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog.
What is EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog?
The EDI 832 formally known as EDI X12 832 Price/Sales Catalog Transaction Set is a critical document that is used to provide product information and pricing data; it is sent from suppliers to buyers. It contains detailed information about the products, including product description, pricing, and other relevant details.
The EDI 832 document is used in various industries, including retail, wholesale, and manufacturing. The document is particularly useful for suppliers who sell a large number of products and need to provide customers with up-to-date information about their products and pricing.
EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog Business Flow
The EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document flow typically involves the following steps:
- Creation. The supplier creates the EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document, which contains information about their products, pricing, and other relevant details.
- Transmission. The EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document is transmitted electronically from the supplier to the buyer.
- Processing. The buyer receives the EDI 832 and processes the information to update their internal business systems, such as their ERP, or inventory management system.
- Update. The supplier updates the EDI 832 every pre-defined period with any changes to product information or pricing, and transmits the updated document to the customer.
- Usage. The buyer uses the information in the EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document to make purchasing decisions and manage their supply chain operations.
This document flow ensures that both the supplier and customer have access to the most up-to-date information, which helps to improve the accuracy and efficiency of supply chain operations.

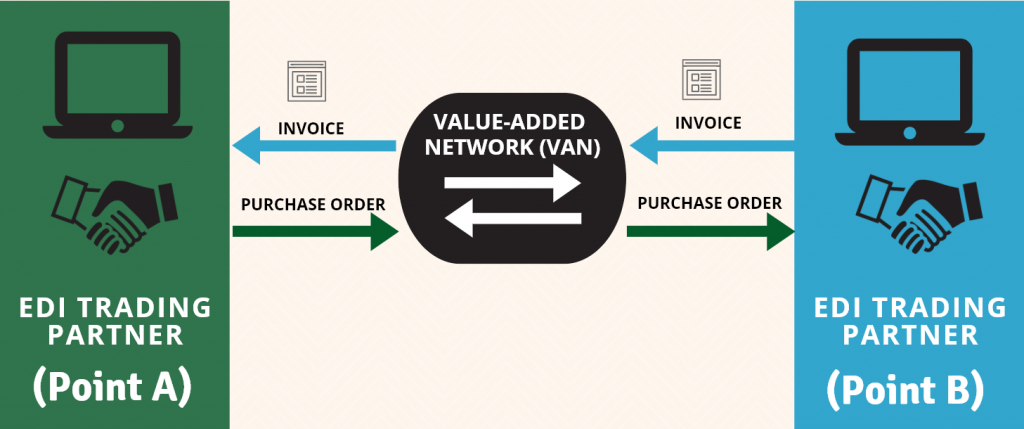
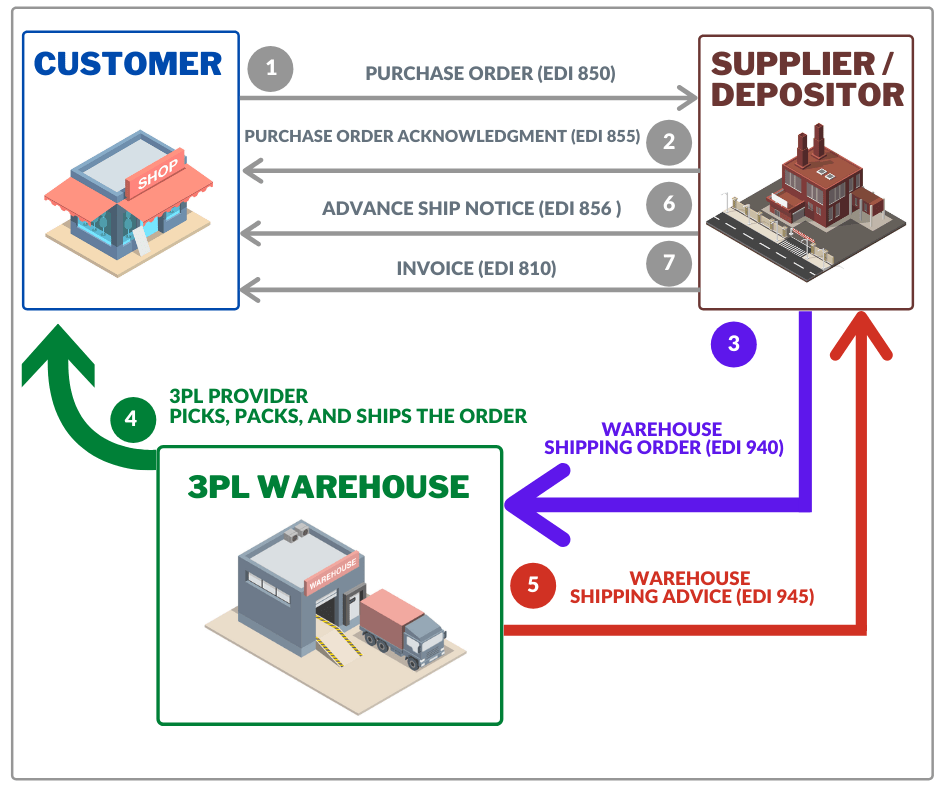
EDI 832: Related EDI Transactions Process Workflow
The EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog process workflow typically involves several related EDI transactions, including the following:
Price/Sales Catalog (EDI 832): The document includes product description, pricing information, and other relevant details.
Purchase Order (EDI 850). The EDI 850 transaction is used to place an order with a supplier. Typical purchase orders include information about the products, quantities, and delivery dates.
Advance Ship Notice (EDI 856). The EDI 856 transaction is used to provide advance notice of a shipment, including information about the items being shipped, the shipping method, and the expected delivery date.
Invoice (EDI 810). The invoice typically includes information about the products being invoiced, the quantities being invoiced, and the total amount due.
These transactions work together to support the complete order-to-payment process, allowing companies to exchange business transactions electronically and streamline their operations.
Key Data Elements in EDI 832
The key data elements in EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document include:
Product Identification: This includes information such as the product code, product name, and product description.
Pricing Information: This includes information such as the unit price, discount information, and any applicable taxes or fees.
Availability Information: This includes information about the availability of the product, including the expected delivery date, lead time, and minimum order quantity.
Product Characteristics: This includes information such as the product dimensions, weight, and any relevant specifications.
Product Classification: This includes information about the product’s classification, such as its category, subcategory, and any relevant product codes.
These key data elements provide the customer with the information they need to make informed purchasing decisions and manage their supply chain operations effectively.
Moreover, since the information is transmitted in a standardized format, it can be easily processed and understood by both suppliers and customers, reducing the likelihood of misunderstandings or errors.
USEFUL READING: Business Automation: How to Choose the Right EDI Solution
EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog –Standards
The EDI 832 price/sales catalog uses the EDI ANSI X12 standard. The ANSI X12 standard is widely used for EDI transactions in the US and North America.
The analog of the X12 EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog transaction set in the EDIFACT PRICAT (Price Catalog) message. EDIFACT Standard is an international standard that is used for Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transactions worldwide but is particularly popular in Europe.
Both the EDIFACT PRICAT message and the X12 EDI 832 document are used to exchange product and pricing information between suppliers and customers. Both standards ensure that the information is transmitted in a standardized format.
EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog – Structure
The structure of the EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document typically includes the following elements:
Header: The header contains information about the sender and receiver of the document, as well as the date and time it was transmitted.
Product Information: This section contains detailed information about the products, including product descriptions, pricing, and other relevant details.
Footer: The footer contains a summary of the information in the EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document, as well as any relevant checksums or error codes.
As stated above, the EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog document adheres to EDI standards, which ensures that the information is transmitted in a standardized format that can be easily processed and understood by both suppliers and buyers. This helps to reduce the likelihood of misunderstandings or errors and ensures that the information is transmitted accurately and efficiently.
IMPORTANT NOTE: The EDI X12 standard does not have the capability to transmit images. The EDI X12 832 Price/Sales Catalog is used to exchange product catalog data, including product descriptions, pricing information, and item specifications. It is a text-based format that is used to transmit data in a standardized format, but it does not have the capability to transmit images or other binary data.
EDI 832 Example
ISA*00* *00* *12*4506813009 *ZZ*RECEIVER *220417*1132*U*00401*700005483*0*P*>~
GS*SC*9372915040*RECEIVER*20220417*113200*700005483*X*004010~
ST*832*1013327~
BCT*RC*126462263313********02~
REF*IA*009824~
DTM*007*20210423~
CUR*SE*CAD~
LIN**VA*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*EN*8051730951638*CM*410*VN*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*SM*1~
REF*PG~
REF*DP~
PID*F*08***JACKET****EN~
PID*F*PG***F21~
PID*F*SC****ME~
PID*F*SIZ***S~
CTP**RES*1495*1*EA~
CTP**WHL*598~
LIN**VA*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*EN*8051730951645*CM*410*VN*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*SM*1~
REF*PG~
REF*DP~
PID*F*08***JACKET****EN~
PID*F*PG***F21~
PID*F*SC****ME~
PID*F*SIZ***M~
CTP**RES*1495*1*EA~
CTP**WHL*598~
LIN**VA*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*EN*8051730951652*CM*410*VN*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*SM*1~
REF*PG~
REF*DP~
PID*F*08***JACKET****EN~
PID*F*PG***F21~
PID*F*SC****ME~
PID*F*SIZ***L~
CTP**RES*1495*1*EA~
CTP**WHL*598~
LIN**VA*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*EN*8051730951669*CM*410*VN*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*SM*1~
REF*PG~
REF*DP~
PID*F*08***JACKET****EN~
PID*F*PG***F21~
PID*F*SC****ME~
PID*F*SIZ***XL~
CTP**RES*1495*1*EA~
CTP**WHL*598~
LIN**VA*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*EN*8051730951676*CM*410*VN*D70GBTD06 MAG0D030*SM*1~
REF*PG~
REF*DP~
PID*F*08***JACKET****EN~
PID*F*PG***F21~
PID*F*SC****ME~
PID*F*SIZ***XXL~
CTP**RES*1495*1*EA~
CTP**WHL*598~
CTT*5~
SE*52*1013327~
GE*1*700005483~
IEA*1*700005483~
How Supply Chain Management Benefits From EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalogs
The EDI 832 document helps buyers to manage their supply chain operations more effectively by providing them with accurate and up-to-date information about the products they purchase. This information can be used to update internal ERP system, such as NetSuite, SAP, Dynamics 365, Salesforce, or other which helps to improve the efficiency of supply chain operations.

Furthermore, both trading partners benefit from the following:
Reduce time, effort, and errors
By using the EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog, companies save time and effort when processing orders and making changes to product information. Using the EDI 832 eliminates the need for manual data entry, which can be time-consuming and error-prone.
Additionally, since the information is in a standardized format, (ex. X12 or EDIFACT) it can be easily integrated into internal business systems such as ERP, reducing the chance of misunderstandings or errors.
Accuracy and efficiency of supply chain
Another important benefit of EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalog is that it helps to improve the accuracy and efficiency of supply chain operations. By providing real-time information about product availability, pricing, and other relevant details, it helps to ensure that orders are processed quickly and accurately, reducing the risk of delays or mistakes. Moreover, since the information is updated regularly, it ensures that suppliers and customers always have access to the most up-to-date information, which helps to improve the overall efficiency of supply chain operations.
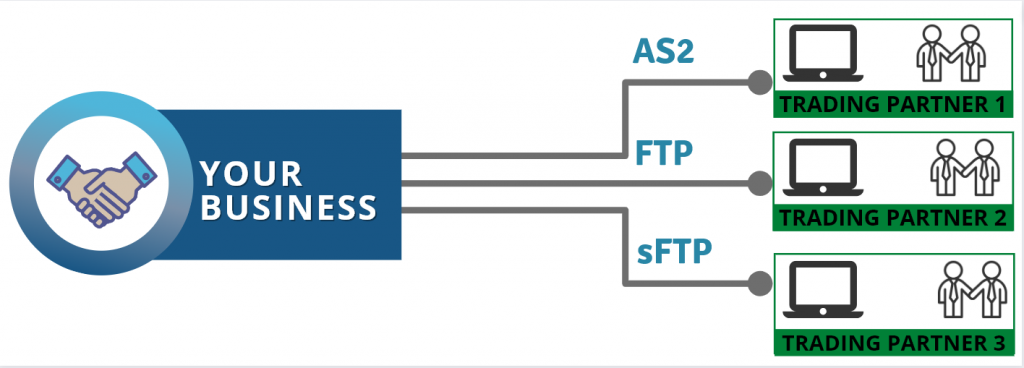
What is the Best Way to Exchange EDI 832?
If you’re looking to start exchanging EDI 832 Price/Sales Catalogs with your trading partners, consider working with a fully managed EDI services provider. With a managed EDI solution, you can streamline your EDI operations and minimize the time and resources required to manage your EDI transactions.
A fully managed EDI solution can handle all aspects of EDI processing, including data mapping, EDI translation, error resolution, and communication with your trading partners. You can focus on your core business while the EDI service provider takes care of the technical details of EDI.
By working with an EDI provider such as EDI2XML, you can enjoy the benefits of EDI 832 without having to invest in software or IT infrastructure. Plus, with experienced EDI professionals handling your EDI operations, you can be confident that your EDI transactions are accurate, timely, and secure.
In conclusion, starting to exchange EDI 832 with a fully managed EDI services provider is a smart way to streamline your EDI operations and ensure that your EDI transactions are handled efficiently and effectively.
Contact us today for your free EDI consultation!