How does EDI2XML work?
In simple terms, EDI2XML is a converter from EDI X12 format to XML format. The result XML format file is based on a pre-defined schema (xsd); we call it our “EDI2XML format”. Here is a very simple graphical description of the EDI2XML engine “in action”.
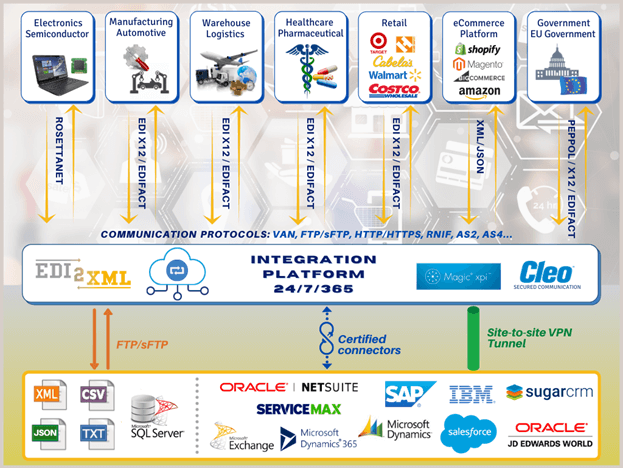
EDI2XML can work in two directions by changing a little switch when executing the command:
- Convert incoming EDI X12 files to XML format
- Convert outgoing XML format files to EDI format
For incoming EDI files, after a raw X12 EDI file is received using communication software and the EDI2XML engine is triggered, the following actions are executed one after the other:
– EDI2XML will verify the structure of the received file to make sure it is a valid raw EDI X12 format file
– If the raw EDI X12 file is valid in terms of structure, it will run another path to eliminate any information not considered part of EDI; for example, some headings and footers sent through the EDI VAN are automatically cleaned as it does not relate to any business information exchanged with the EDI partner
– The engine is smart enough to split a batch of incoming EDI files inside the same physical file, by envelop (ISA) and by ISA id, as a preparation for the conversion to XML, regardless of its EDI standard and revision
– Once all of the above is completed, the engine would generate for each one of the EDI files an equivalent XML formatted file.
The EDI2XML engine works a little differently when converting raw X12 files from an XML format. Once the engine is triggered with the option to convert XML to EDI X12 format, it will do the following actions:
– For each XML file found, EDI2XML will validate its structure and find out if it is well formed, to make sure it is compliant with edi2xml format and schema
– For each valid XML file, the engine will convert from XML to X12 raw EDI format
*It is important to note that the XML file should comply with a pre-defined xsd (or schema). All necessary information related to EDI versions and standards are sent within the XML file. For incoming and outgoing edi2xml formatted files, only files from the “ licensed” partners are being processed. Any EDI or XML file sent from/to an unlicensed partner will NOT be processed at all.



